Nodular Cast Iron Grate,Ductile Cast Iron Anti-Precipitation Grate,Ductile Cast Iron Anti-Settling Grate,Square Nodular Cast Iron Anti-Precipitation Grate Wuan Jianfeng Casting Co., Ltd. , https://www.hbjfcasting.com
Intro to Relays #1 - What are Relays, CTs & PTs?
Protective relays are a critical and complex area of electrical engineering, especially in the solar and energy storage industries. While they may seem intimidating at first, this three-part series aims to simplify the basics for non-engineers who work in these fields.
**Intro to Relays #1 – What are Relays, CTs, & PTs? (below on this page)**
**Intro to Relays #2 – ANSI/IEEE Relay Device Numbers**
**Intro to Relays #3 – What does SEL stand for?**
**What is a Relay?**
In the context of solar and energy systems, a "relay" typically refers to a "protective relay." These devices monitor key electrical parameters like voltage, current, and frequency. When an abnormal condition is detected, the relay triggers a switch to isolate the affected part of the system, preventing damage or further issues.
Historically, relays were mechanical, electromagnetic devices. Today, most modern relays are microprocessor-based, essentially functioning as small computers that can process data and make decisions in real time.

**Function of a Relay**
The main purpose of a protective relay is to quickly remove faulty equipment from service to prevent damage and maintain system stability. They protect the electrical system in two primary ways:
1. **Prevent damage:** By detecting and responding to abnormal conditions before they cause harm.
2. **Mitigate impact:** If a fault occurs, the relay ensures it doesn’t spread or cause more extensive problems.
Relays continuously monitor the electrical circuit and look for deviations from normal operating conditions. When a threshold is exceeded, the relay sends a signal to a switching device—like a circuit breaker—to either open or close the circuit, depending on the situation.
These relays can protect various components, including:
- Solar PV systems
- Energy storage systems
- Building electrical infrastructure
- The utility grid
For example, an overcurrent relay can detect excessive current on a feeder line and trigger a circuit breaker to cut off power. A reverse power relay prevents backfeeding into the grid beyond safe limits, protecting both the solar system and the utility’s equipment.
An overvoltage relay helps safeguard inverters and transformers by disconnecting the system if a voltage spike is detected.
**Attention Engineers!**
If you enjoy diving deep into technical topics like this, you might be a great fit for Pure Power. Our team of 80 engineers has designed over 2,000 commercial and utility-scale solar projects. Working alongside such experienced professionals can help you grow your career and expand your knowledge. Check out our open positions today!
**How is a Relay Different from a Circuit Breaker or Fused Switch?**
While circuit breakers and fused switches also interrupt current when it becomes too high, their functionality is limited. They’re primarily overcurrent protection devices with little to no adjustability.
In contrast, a relay offers much greater flexibility and intelligence:
- **Multi-function monitoring:** Relays can track current, voltage, frequency, power factor, and more. This is especially important in solar systems where grid compatibility is crucial.
- **Custom programming:** Each relay can be programmed to respond differently based on the project's needs, even if the same model is used across multiple sites.
- **Modular design:** Unlike a circuit breaker, which is a single unit, a relay often includes separate components like CTs, PTs, and a switching device, allowing for more tailored integration.
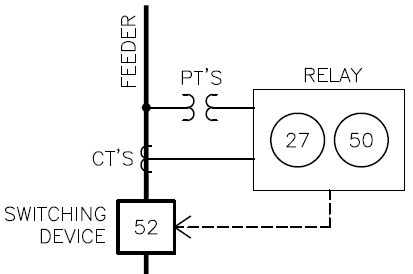
**What are Current Transformers (CTs)?**
Current Transformers, or CTs, are used to measure high currents in a circuit safely. Since the actual current in a system can be far too high for a relay to handle directly, CTs step it down to a manageable level—like 800:5, which means 800 amps are reduced to 5 amps for the relay.

**What are Potential Transformers (PTs)?**
Potential Transformers, or PTs, serve a similar purpose but for voltage and frequency. They reduce high voltages to a level that can be safely measured by the relay, ensuring accurate monitoring without risking damage.

**Switching Device**
The switching device is what actually opens or closes the circuit. In utility-scale systems, this could be a vacuum circuit breaker or recloser. In smaller commercial systems, it might be a 480V or 208V circuit breaker with a shunt trip option.
**Conclusion**
At a high level, relaying seems straightforward, but the details can get quite complex. For project managers and developers, understanding every technical nuance isn’t always necessary. That’s where experienced engineers come in. At Pure Power, we specialize in designing and implementing reliable relay systems for solar and storage projects. If you need assistance with your next project, reach out today and let us help you ensure safety and performance.
Next Article
CFD 3-11 on 3-5-11
Prev Article
Apartment fire in Wheeling 11-10-11